Photobiology
Solar UV radiation can generate damaging free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cells and tissues. Production of free radicals and ROS can lead to inflammation, premature aging disorders, and several disease states, including cancer, diabetes, and atherosclerosis. Topical treatments, formulations and therapeutics can help prevent these damaging effects and reduce cellular stress.
Zen-Bio offers several methods for evaluating test samples, formulations and compounds for their effects in the presence of UV-A and/or UV-B, visible light or infrared exposure.
| Skin sample | Cells, RHE or explant |
| PreTreatment | Test Samples variable time |
| UV Treatment | Variable dose UVA/B |
| Readout(s) | ELISA qPCR |
| Endpoint(s) | Cytokine secretion Transcriptional changes |

Cytokine secretion in human RHEs is induced by UVB exposure and blocked by sunscreen
UV-induced Cellular DNA Damage
Solar UVB radiation can induce mutagenic DNA damage in cells that may result in skin cancer. The UV-induced cellular DNA damage assay can measure a test sample's ability to modulate cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer (CPD) formation (DNA damage) caused by UVB exposure in human cells or reconstituted human epidermis (RHE) models.
| Skin sample | Any cell type, Fibroblasts Keratinocytes, Melanocytes RHE |
| Format 96-well plate, RHE | |
| PreTreatment | Test samples for 1 hour |
| Treatment | Variable dose UVB |
| Readout | cellular CPD staining |
| Endpoint(s) | IC50 concentration Percent inhibition |

CPD formation (red) in human keratinocytes exposed to UVB
Cellular ROS Formation
Solar radiation can produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) in human skin cells which can react with surrounding proteins, lipids or small molecules causing cellular damage and inflammation. The cellular ROS formation assay is a method to test the ability of a sample to modulate the amount of ROS generated in cultured cells by UV radiation.
| Cells | Dermal Fibroblasts "Keratinocytes |
| Other | cell types" |
| Format | 96-well plate |
| PreTreatment | Test samples for 1 hour |
| Treatment | UVA, UVB, IR |
| Readout | cellular ROS staining |
| Endpoint(s) | IC50 concentration Percent inhibition |
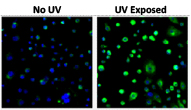
ROS formation (green) in human keratinocytes exposed to UVB
In Vitro RHE Phototoxicity
The in vitro reconstructed human epidermis (RHE) phtotoxicity assay (OECD 498) is a method to evaluate the phototoxic potential of a sample on a model human epidermis.
| Cells | Human stratified keratinocytes |
| Format | RHE |
| PreTreatment | Test samples for 18-24 hours |
| UV Treatment | 6 J/cm2 UVA |
| Readout | MTT |
| Endpoint(s) | Percent viability Phototoxic potential |

Viability of chlorpromazine-treated RHEs with and without UVA exposure
3T3 NRU Phototoxicity
The 3T3 neutral red uptake (NRU) phototoxicity assay (OECD 432) is a method to test the concentration-dependent cytotoxicity of a sample on Balb/c 3T3 fibroblasts with and without exposure to 5 J/cm2 UVA light.
| Cells | Balb/c fibroblasts |
| Format | 96-well plate |
| PreTreatment | Test samples for 1 hour |
| Treatment | 5 J/cm2 UVA |
| Readout | Neutral Red Uptake |
| Endpoint(s) | IC50 concentration Photo-Irritation Factor (PIF) Mean Photo Effect (MPE) |

Viability of chlorpromazine-treated Balb/c 3T3 cells with and without UVA exposure
Photostability
Compounds can undergo degradation when exposed to solar UV light which can decrease their therapeutic efficacy and potentially create ROS or cytotoxic degradation products. This method is used to test the effects of variable UVA/UVB energy to induce degradation of a sample monitored by its absorbance and/or fluorescence spectra.
| Format | 96- or 384-well |
| UV Treatment | Variable UVA or UVB |
| Readout(s) | Absorbance spectrum Fluorescence spectra |
| Endpoint(s) | Absorbance spectrum Fluorescence spectra |

Absorbance spectra of aspirin with and without UVB exposure

Fluorescence excitation and emission spectra of aspirin after UVB exposure
To learn more about our services or get a price quote, please contact our Services Team or call ZenBio. Prices for contract services vary depending on number of sample numbers, special conditions, compound solubility, etc. Minimum charges will apply.



